! ! WARNING ! !
Above is Zulu Time!!
The Airbus A380 was developed in response to the growing problems of airport congestion and air traffic control systems struggling to cope with the number of aircraft in operation. Originally known as the A3XX, the enormous design was re-christened as the A380 following the official launch of the program in late 2000. Upon entering service, the A380 will become the first full triple-decked super jumbo-jet as well as the first true competitor to the Boeing 747. Though many argue that the aviation industry is not ready for such a giant, Airbus believes that by commiting to the A380 now, the company will be in excellent position to take advantage of such a need by 2020. By then, Airbus estimates a potential need for 1,200 passenger and 300 freighter models.
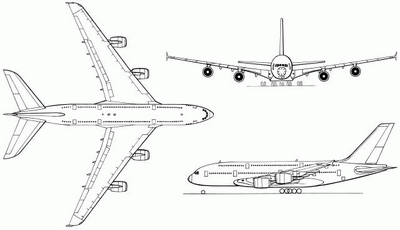
Despite its large size, the A380 adopts a conventional airliner design with a cylindrical fuselage slightly wider than that of the 747. The A380 also features a low-mounted swept-wing with four podded engines along its span. The landing gear of the A380 feature 22 wheels so that the load per wheel is comparable to that of the Boeing 747 and 777. This design makes the A380 compatible with most existing runways at major airports. However, the large wingspan of the A380 requires most airports to widen taxiways so that two planes can pass each other. In addition, many airports must add additional jetway bridges to accomodate the large number of passengers, and baggage handling systems also need to be upgraded. A handful of airports at major international hubs are investing millions of dollars to hurriedly complete these improvements by the time the A380 enters service.
The internal layout of the A380 is of typical configuration with passengers seated on the two upper decks and cargo located on the lower deck. Airbus has also proposed configuring some cargo compartments as shops, lounges, or even casinos, although economy-minded airlines are unlikely to adopt such gimics. The flight deck is very similar to that of the A330/A340 family to ease A380 pilot training and promote commonality across the Airbus production line. Furthermore, the cockpit is located in between the upper and main decks at a height comparable to that of smaller airliners for easier pilot familiarity.
Two basic models are currently being marketed, the A380-800 passenger model seating up to 555 in three classes and the A380-800F freighter version. Additional extended range, passenger/cargo, and stretched models are also under consideration. A total of 14 customers had placed orders for nearly 150 aircraft by the end of 2004. Unfortunately, difficulties in manufacturing have delayed A380 deliveries and pushed service entry back by at least a year to late 2006 or early 2007. These delays have also caused a significant cost overrun of nearly $1.5 billion driving up A380 unit cost by about 25%.
Data below for A380-800 and A380-800F
Last modified 19 November 2005
HISTORY:
First Flight (A380-800) 27 April 2005
(A380-800F) planned for early 2007
Service Entry
(A380-800) planned for 2006 or 2007 (with Singapore Airlines)
(A380-800F) planned for 2008 (with Federal Express)
CREW: two flight crew: pilot, co-pilot
PASSENGERS: (A380-800) 555 in three classes, 840 in one class
ESTIMATED COST: $263 to $286 million [2005$]
AIRFOIL SECTIONS:
Wing Root unknown
Wing Tip unknown
DIMENSIONS:
Length (A380-800) 238.67 ft (72.75 m)
Wingspan 261.83 ft (79.80 m)
Height 79.00 ft (24.08 m)
Wing Area 9,095.5 ft2 (845.0 m2)
Canard Area not applicable
WEIGHTS:
Empty (A380-800) 610,680 lb (277,000 kg)
(A380-800F) 555,565 lb (252,000 kg)
Normal Takeoff unknown
Max Takeoff (A380-800) 1,234,590 lb (560,000 kg)
(A380-800F) 1,300,725 lb (590,000 kg)
Fuel Capacity internal:
(A380-800) 575,185 lb (260,900 kg)
(A380-800F) 575,185 lb (260,900 kg)
external: not applicable
Max Payload (A380-800) 185,190 lb (84,000 kg)
(A380-800F) 330,695 lb (150,000 kg)
PROPULSION:
Powerplant (A380-800) four Rolls-Royce Trent RB-967 turbofans
or four Engine Alliance GP-7267 turbofans
(A380-800F) four Rolls-Royce Trent RB-975 turbofans
or four Engine Alliance GP-7275 turbofans
Thrust (A380-800 RB-967) 272,000 lb (1,210 kN)
(A380-800 GP-7267) 326,000 lb (1,450 kN)
(A380-800F RB-975) 299,435 lb (1,332 kN)
PERFORMANCE:
Max Level Speed at altitude: 595 mph (955 km/h) at 35,000 ft (10,675 m), Mach 0.89
at sea level: 390 mph (630 km/h)
cruise speed: 560 mph (900 km/h) at 35,000 ft (10,675 m), Mach 0.85
Initial Climb Rate unknown
Service Ceiling 42,980 ft (13,100 m)
Range (A380-800) 8,000 nm (14,815 km)
(A380-800F) 5,600 nm (10,370 km)
g-Limits unknown
KNOWN VARIANTS:
A380-700 Originally known as the A3XX-50 or A3XX-50R, proposed extended range model with a shortened fuselage for 481 passengers
A380-800 Originally known as the A3XX-100, first production model seating 555 passengers
A380-800C7 Proposed combination passenger/cargo model based on the A380-800 with space for 7 cargo pallets
A380-800C11 Proposed combination passenger/cargo model with space for 11 cargo pallets
A380-800F Originally known as the A3XX-100F, dedicated freighter based on the A380-800 model with a capacity of 25 pallets on the upper deck, 33 pallets on the main deck, and 13 pallets on the lower deck
A380-800R Proposed extended range model based on the A380-800 for 555 passengers
A380-800S Proposed reduced range version of the A380-800
A380-900 Originally known as the A3XX-200, proposed stretch model with a longer fuselage for 656 passengers
A380-900S Proposed reduced range version of the A380-900
KNOWN OPERATORS: Air France
Emirates Airlines
Etihad Airways
Federal Express
International Lease Finance Corporation (ILFC)
Lufthansa
Kingfisher Airlines
Korean Air Lines
Malaysian Airline System
Qantas
Qatar Airways
Singapore Airlines
Thai Airways
United Parcel Service (UPS)
Virgin Atlantic Airways
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
Article last modified on 10/06/2015

|

|
|
(c) 2004 www.simbuilder.be Created by See3D.be |
||

